No, urticaria is not contagious. It is not caused by a virus or bacteria and cannot be transmitted from person to person.

12/05/2023

Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the appearance of itchy, raised welts on the skin. These welts can vary in size and shape and are usually accompanied by redness and swelling. Urticaria is a highly prevalent condition, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. Despite its prevalence, the exact causes and mechanisms behind urticaria remain to be fully understood.
( Unlock a free expert doctor consultation here... )
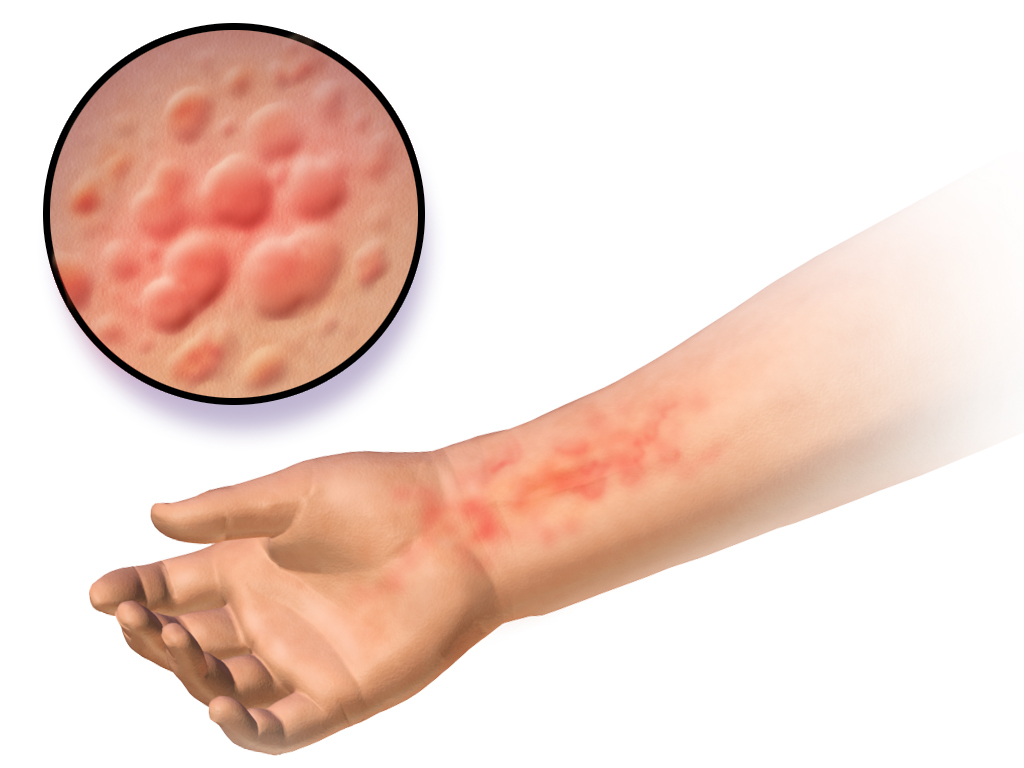
Acute urticaria is a short-term condition that typically lasts for a few hours to several weeks. It is often caused by allergic reactions to certain foods, medications, insect bites, or infections. The welts associated with acute urticaria usually disappear within 24 hours but may reappear in different locations.
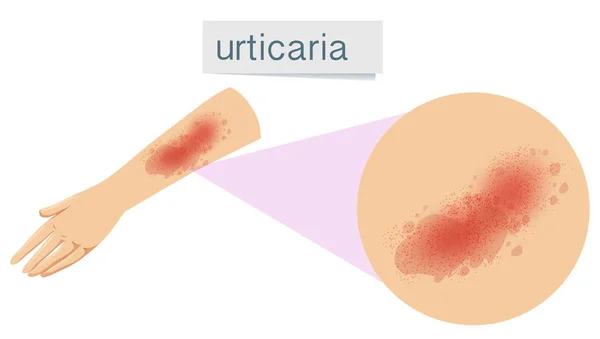
Chronic urticaria, on the other hand, lasts for more than six weeks and can persist for months or even years. The cause of chronic urticaria is often more difficult to identify. It may be associated with underlying medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or hormonal imbalances. Chronic urticaria can significantly impact a person's quality of life, leading to persistent discomfort and frustration.

It's important to note that triggers can vary from person to person, and identifying the specific triggers for an individual is crucial in managing their urticaria effectively.
( Unlock a free expert doctor consultation here... )

The primary symptom of urticaria is the appearance of itchy, raised welts on the skin, also known as hives. These welts can be of varying sizes, ranging from small dots to large patches. They are usually red or pink in color and may have a pale center. The welts can appear on any part of the body and may change shape, fade, or reappear in different locations.
In addition to the physical symptoms, urticaria can also cause discomfort and emotional distress due to the constant itching and appearance of the welts.
Diagnosing urticaria involves a thorough medical history review, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests. The doctor may inquire about potential triggers, recent exposures, or underlying health conditions. Allergy tests or blood tests may be recommended to identify specific allergens or underlying immune system abnormalities.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances.
( Unlock a free expert doctor consultation here... )

Again, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional before relying solely on home remedies for the treatment of urticaria.
( Unlock a free expert doctor consultation here... )

Regular follow-ups with a healthcare professional are essential for monitoring the condition, adjusting treatment plans if necessary, and addressing any concerns or new symptoms.
( Unlock a free expert doctor consultation here... )
No, urticaria is not contagious. It is not caused by a virus or bacteria and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
Yes, emotional stress can sometimes trigger or worsen episodes of urticaria. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can be beneficial in reducing the frequency of flare-ups.
In most cases, urticaria is a temporary condition and does not lead to long-term complications. However, chronic urticaria can significantly impact a person's quality of life and may require ongoing management.
Yes, certain foods can trigger urticaria in susceptible individuals. Common culprits include shellfish, nuts, eggs, and dairy products. Identifying and avoiding these trigger foods can help prevent episodes.
While there is no definitive cure for urticaria, it can be effectively managed with the help of healthcare professionals. Treatment aims to control symptoms and minimize the impact on daily life.
Urticaria, or hives, is a common and often frustrating skin condition characterized by itchy welts on the skin. Despite its prevalence, the exact causes of urticaria are still not fully understood. By identifying triggers, following an appropriate treatment plan, and implementing preventive measures, individuals with urticaria can effectively manage their condition and improve their quality of life. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management of urticaria.